KinePose: A temporally optimised inverse kinematics technique for 6DOF human pose estimation with biomechanical constraints
Introduction
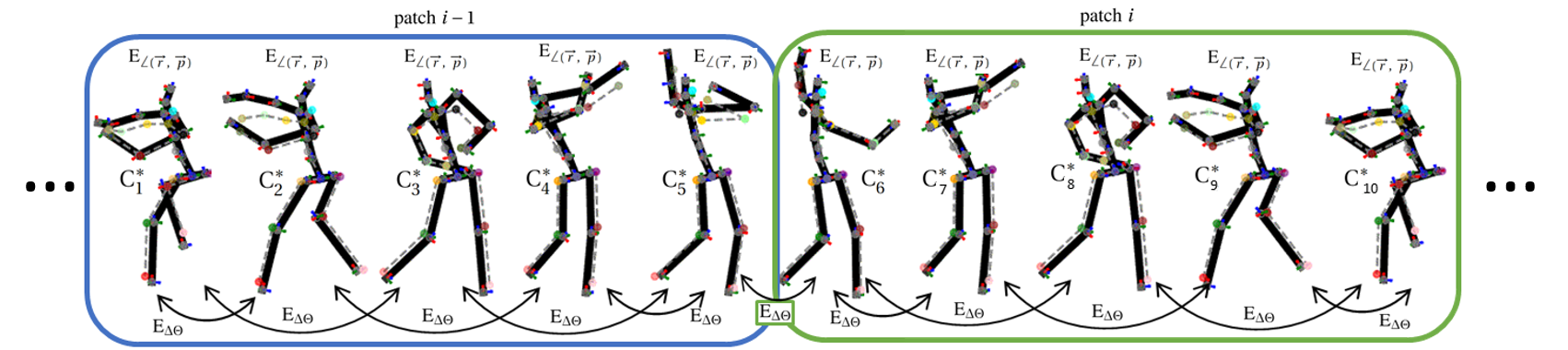
KinePose is an innovative approach for 6 Degrees of Freedom (DOF) human pose estimation, incorporating Inverse Kinematics (IK) with biomechanical constraints. Developed for diverse applications ranging from sports to impact analysis, KinePose offers enhanced biomechanical relevance in monocular human pose estimation.
Tools
For use with the suite of ellipsoid human body models in MADYMO (MAthematical DYnamic MOdels)
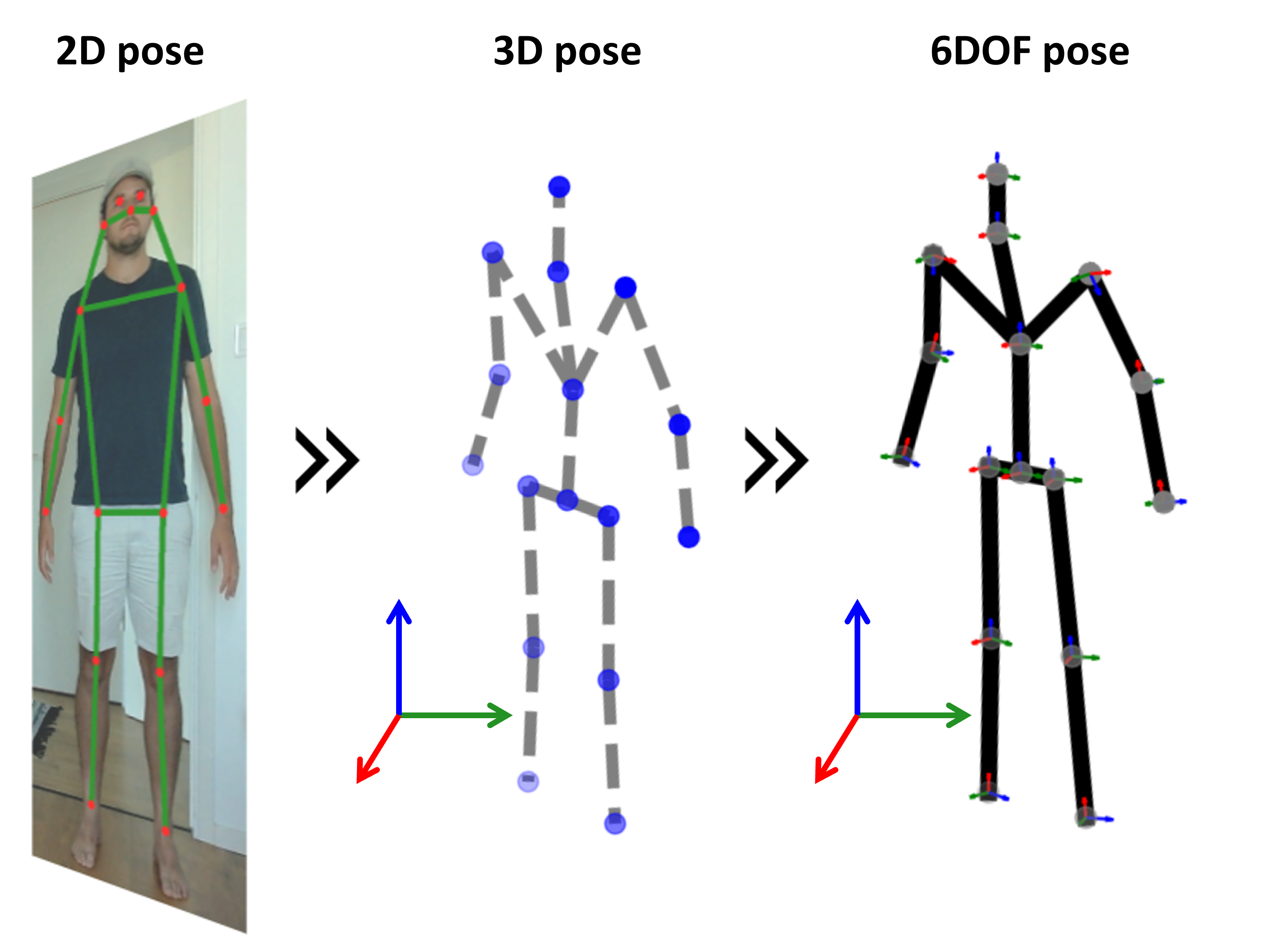
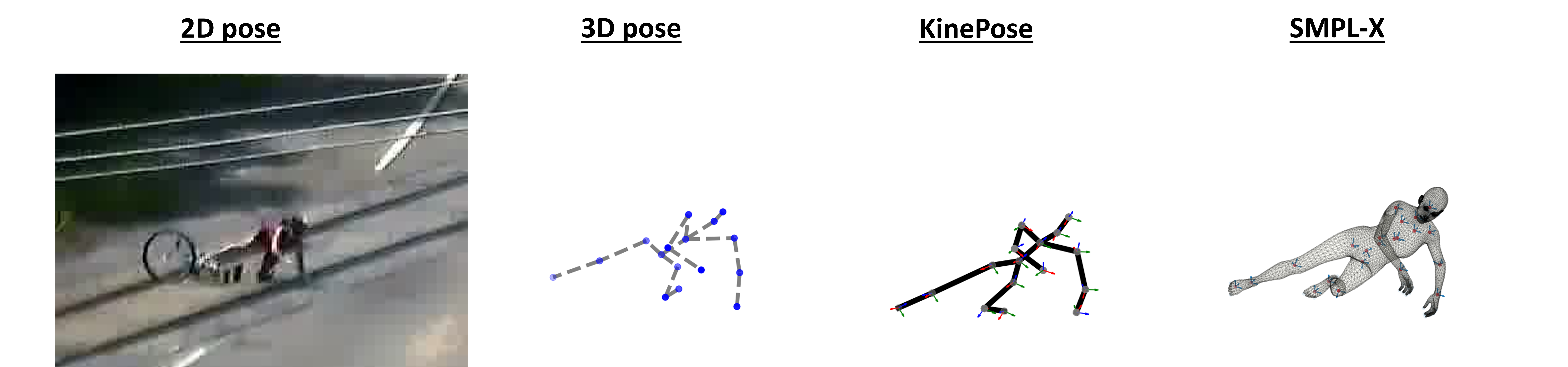
| Step | Description | Tools | Manuals |
|---|---|---|---|
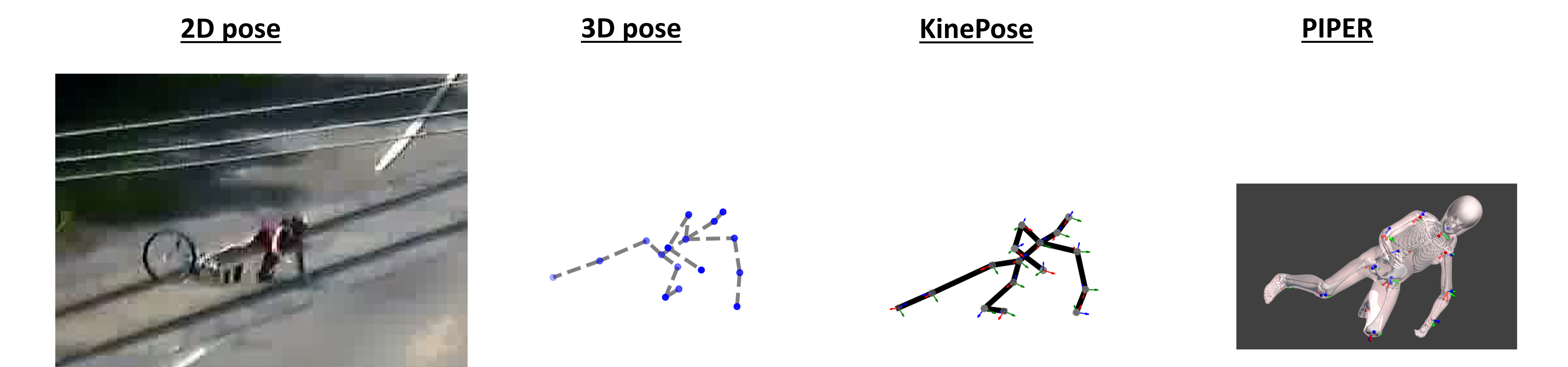
| 2D Pose | Initial pose estimation in pixel coordinates. Options: 1) fully automatic (YOLOv8), 2) semi-automatic with manual refinement, 3) fully manual. |
Tools | TBD |
| 3D Pose | Lifting from 2D to 3D pose (MotionBERT). | Tool | TBD |
| 6DOF Pose | IK optimisation to a 6DOF pose (KinePose). | Tool | TBD |
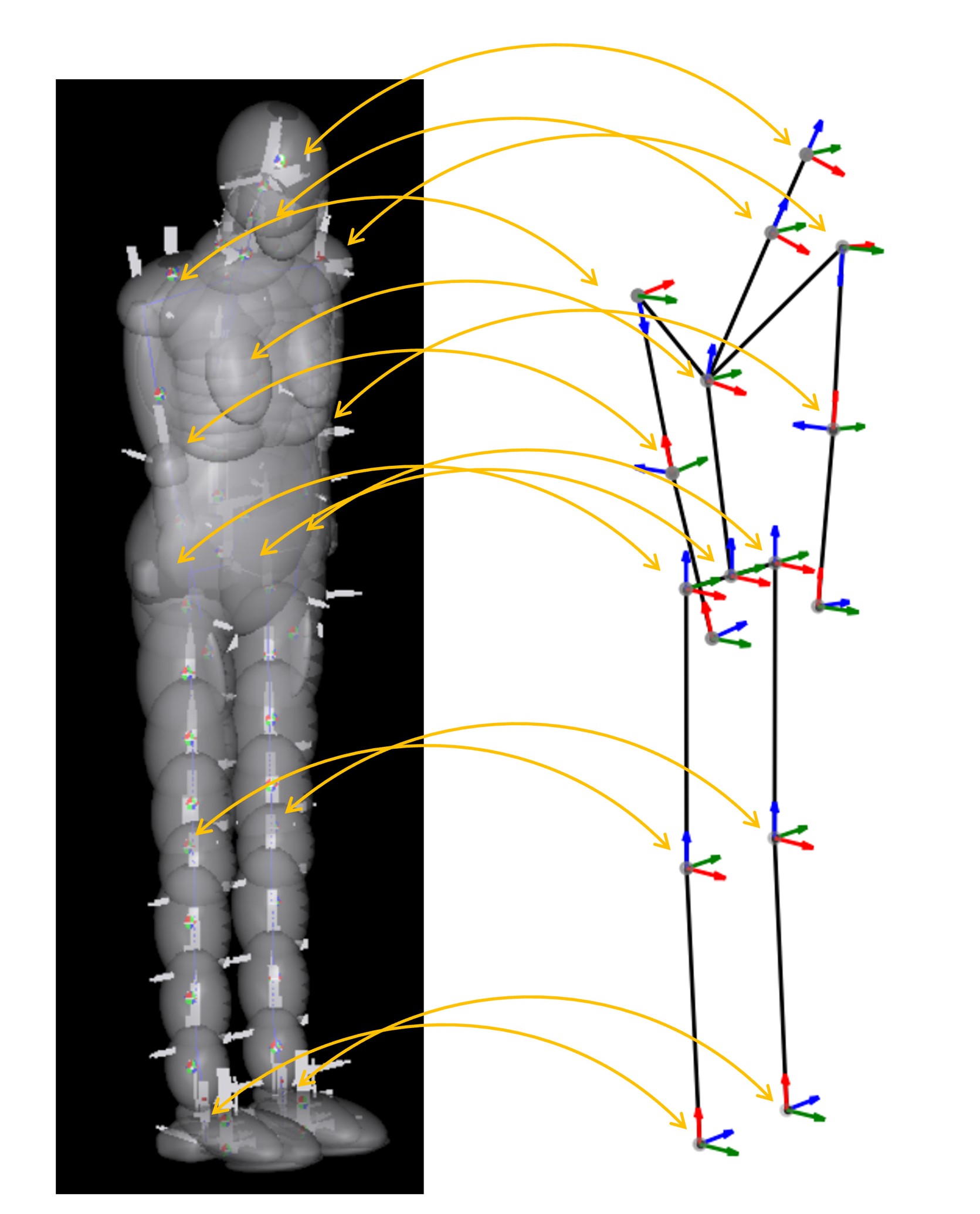
For use with SMPL/SMPL-X
Work in progress…
For use with the PIPER HBM
Work in progress…
For use with VIVA+ HBMs
TBD
For use with the OpenSim HBM
TBD
General-purpose (user customisable biomechanical model)
TBD
Example applications
1) Baseball swing analysis

2) Single bicycle crash reconstruction
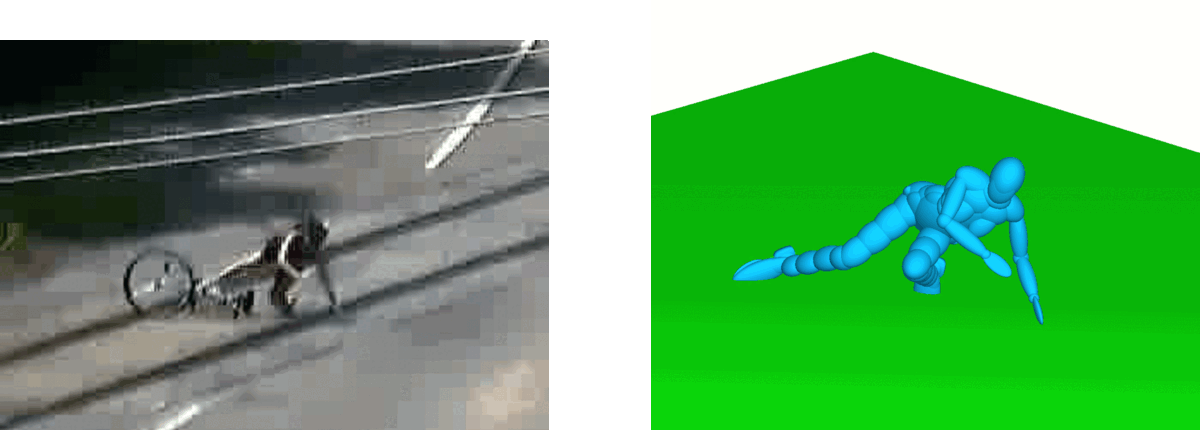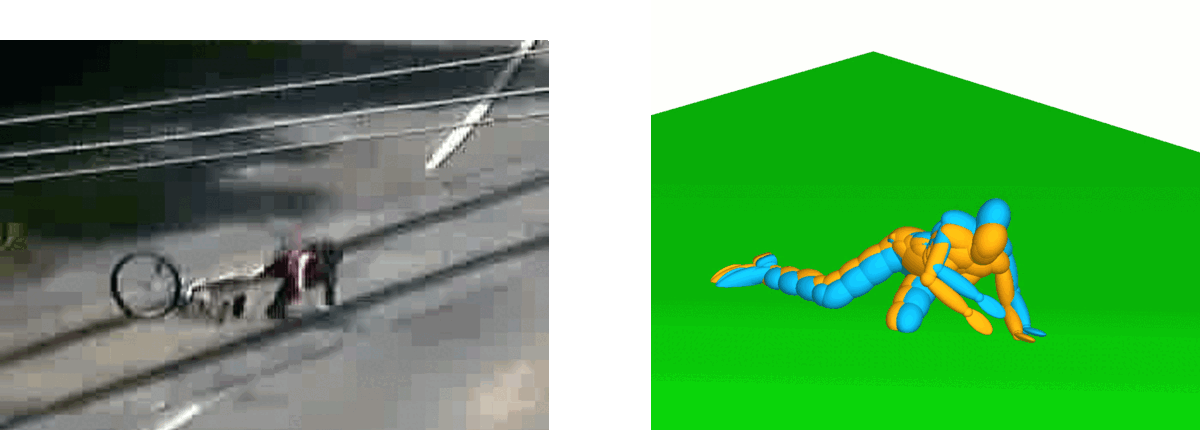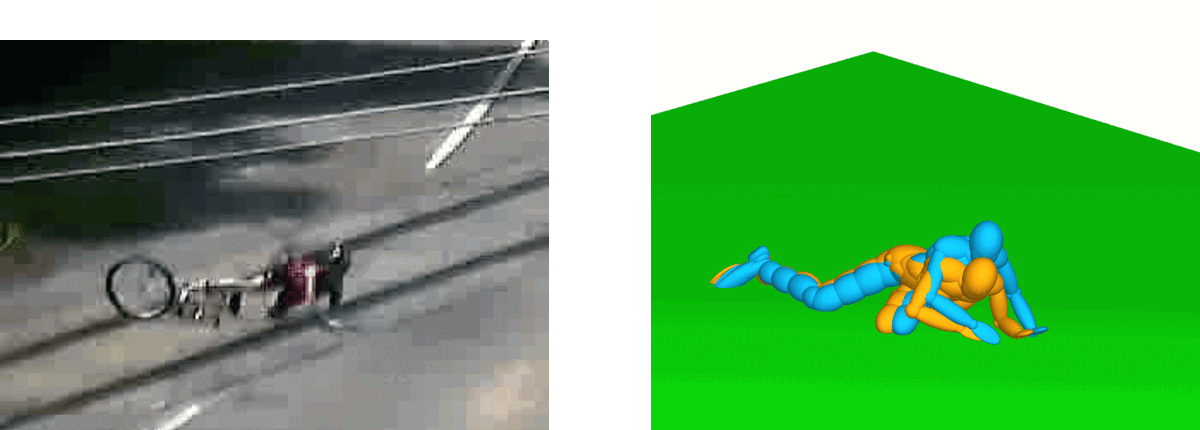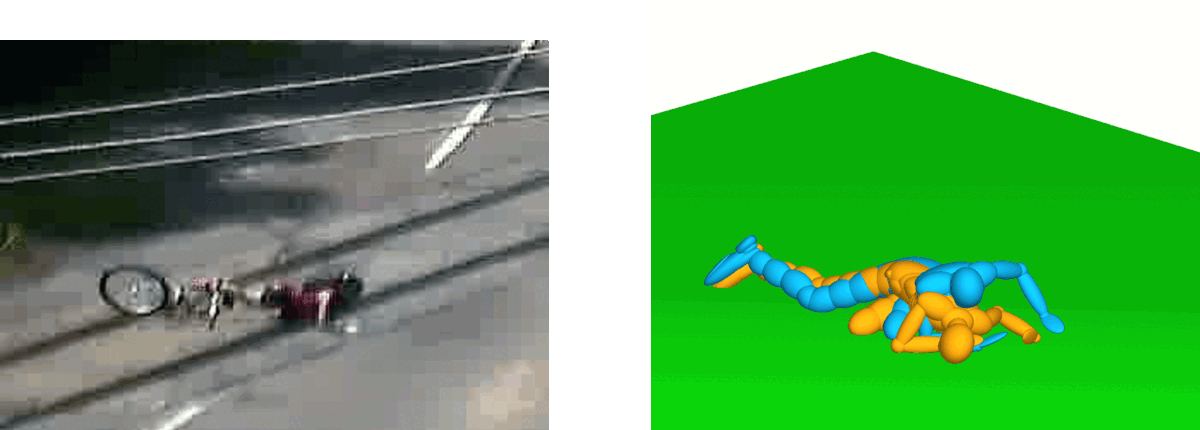
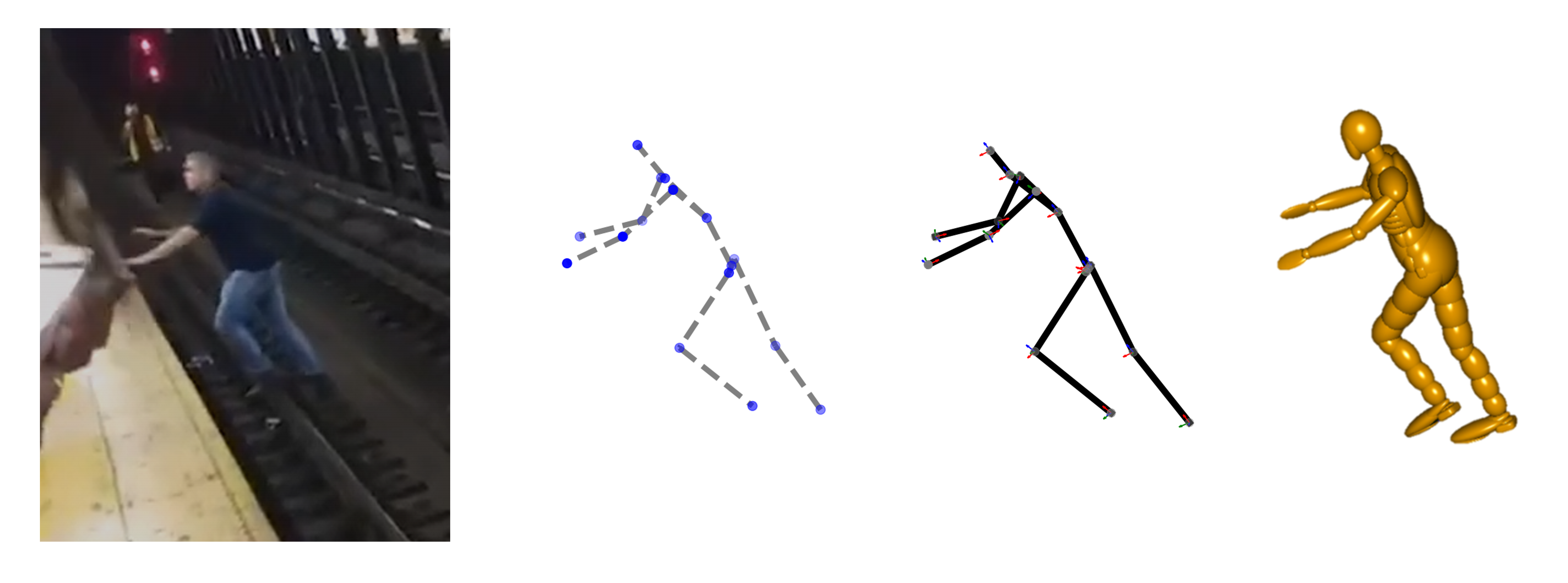
3) Reconstruction of representative pedestrian pre-impact poses
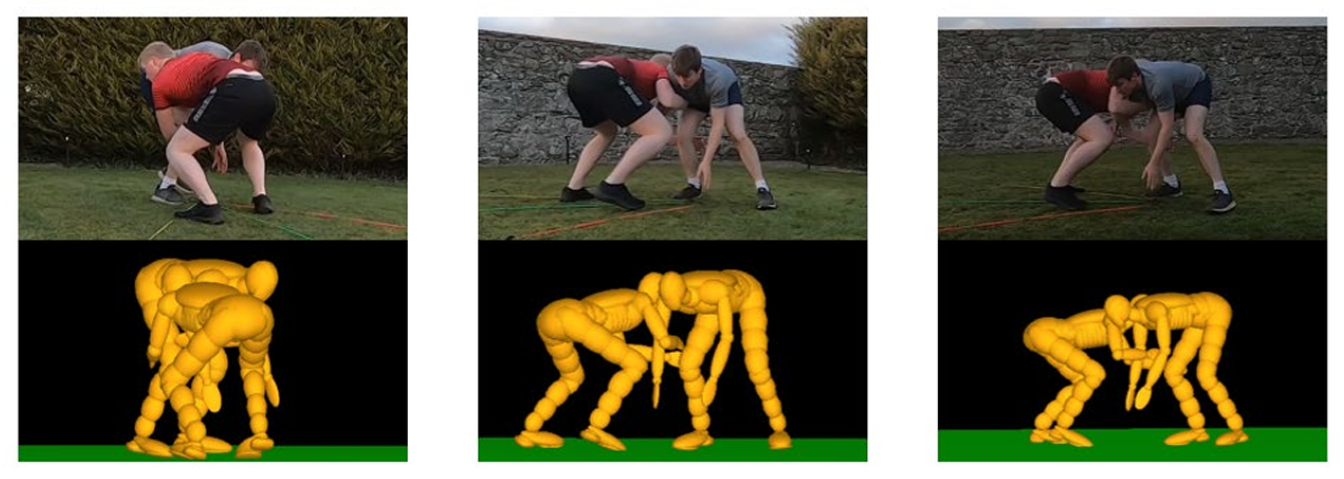
4) Rugby tackling pose estimation and reconstruction

Conference presentations
- Congress of the European Society of Biomechanics (ESB 2022)
- Irish Machine Vision & Image Processing Conference (IMVIP 2022)
Cite our methods papers
If you find KinePose useful in your research, please consider citing our work:
Gildea, K., Mercadal-Baudart, C., Blythman, R., Smolic, A., & Simms, C. (2022). KinePose: A temporally optimized inverse kinematics technique for 6DOF human pose estimation with biomechanical constraints. In Irish Machine Vision & Image Processing Conference (IMVIP). 10.56541/QTUV2945 SuppMat
Gildea, K., Hall, D., Cherry, C., & Simms, C. (2024). Forward dynamics computational modelling of a cyclist fall with the inclusion of protective response using deep learning-based human pose estimation. *Journal of Biomechanics. 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2024.111959
